Apache Hive
17 Feb 2016- Hive Architecture
- Hive Principles
- Data Types
- Hive Basics Query Commands
- Hive Table Partitions and Bucketing

- Data warehouse infrastructure tool to process structured data in Hadoop.
- Provides a SQL like query language and interfaces to Hadoop
- Builds on Hadoop core using MapReduce for execution
- Query execution via Apache Tez, Apache Spark or Map Reduce
Hive Architecture
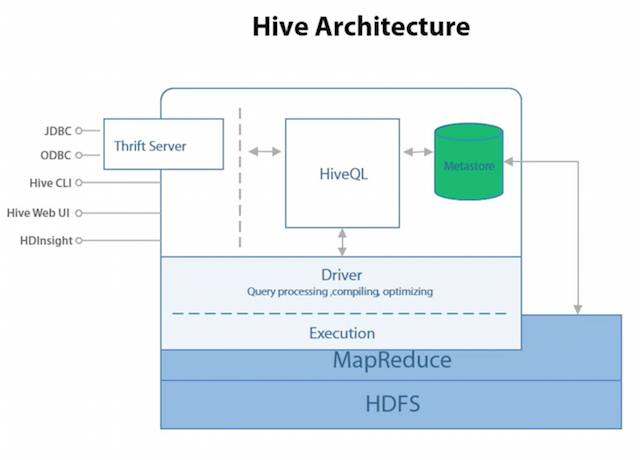
- Data is stored in HDFS
- Stored in Hive Warehouse directory (
hive.metastore.warehouse.dir)
- Stored in Hive Warehouse directory (
- Metastore (Lightweight Derby Database) stores Metadata about the data
- Metastore acts as a bridge between Hive and files in HDFS
- Relational Database (Default: Derby)
- Driver to connect via JDBC, ODBC, Hive CLI, Hive Web UI and HDInsights.
Hive Principles
Schema on Read
Hive Warehouse
- Metadata about all the objects known to Hive, persisted in the meta store
- Consists of Databases, Tables, Partitions and Buckets / Clusters
Hive Tables
- Managed Tables
- Managed by Hive
- Hive owns the files and directories
- Deleting a managed table deletes both data and metadata
- External Tables
- Underlying data is not deleted
- Temporary Tables
- Store temporary data
- Tables of the same name can be created by different user
- Do not support partitions and indexes
Data Types
Primitive Data Types
- BOOLEAN
- Numeric
- Integers (
TINYINT,SMALLINT,INT,BIGINT)
- Integers (
- Decimal
FLOATDOUBLEDECIMAL
- String
String- UnboundedChar- Fixed LengthVarchar- Bounded
- Timestamp
- “YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.fffffff”
- Integer types as UNIX timestamp in second from UNIX epoch
- Dates
Complex / Collection Types
- Arrays [ ARRAY
] - Maps [ MAP<primitive_type, data_type>]
- Struct [STRUCT]
- Union [UNIONTYPE]
Hive Basics Query Commands
The SELECT statement
SELECT exp1, exp2, ...
FROM <table> WHERE <where_condition>
LIMIT N;
- SELECT and FROM are Interchangeable
Sample SELECT Commands
-- Retrieving Information
SELECT from_column FROM table WHERE conditions;
-- All Values
SELECT * FROM table;
-- Multiple Criteria
SELECT * FROM table WHERE rec = "value1" AND rec2="value2";
-- Selecting Specific Columns
SELECT column_name FROM table;
-- Retrieving Unique Output Records
SELECT DISTINCT column_name FROM table;
-- Sorting
SELECT col1, col2 FROM table ORDER BY col2;
-- Sorting (DESC)
SELECT col1, col2 FROM TABLE ORDER BY col2 DESC;
-- Counting Rows
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM table;
-- Grouping with Counting
SELECT owner, COUNT(*) FROM table GROUP BY owner;
-- Maximum Value
SELECT MAX(col_name) as label FROM table;
-- SELECT from Multiple Table
SELECT pet.name, comment FROM pet JOIN event ON (pet.name = event.name);
-- Distinct Clause
SELECT DISTINCT col1,col2,col3 FROM <table>;
-- Aliasing
SELECT col1+col2 AS col3 FROM <table>;
-- Regex Column Specification
SELECT '(ID|Name)?+.+' FROM <table>;
Joins
- Hive support Equi-join only
SELECT c.id, c.name, o.product_id
FROM customers c JOIN orders o
ON (c.id = o.customer_id);
SubQueries and Union
SELECT mycol
FROM (
SELECT col_a + col_b AS mycol
FROM some_table
) subq;
Union All
SELECT col_a + col_b AS mycol
FROM some_table
UNION ALL
SELECT col_c AS mycol
FROM another_table
Create Database
Hive Warehouse
Hive Managed Database
CREATE (DATABASE|SCHEMA) [IF NOT EXISTS] database_name
[LOCATION hdfs_path]
[WITH DBPROPERTIES (property_name=property_value, ....)];
Example,
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS art
LOCATION '/user/admin/art/tst';
Delete Database
DROP (DATABASE|SCHEMA)[IF EXISTS] database_name [CASCADE];
DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS art;
Create Table
CREATE [EXTERNAL] TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] [db_name].table_name
[(col_name datatype [COMMENT col_comment], ...)]
[PARTITIONED BY (col_name datatype [COMMENT col_comment], ...)]
[ROW FORMAT DELIMITED][STORED AS file_format]
[LOCATION hdfs_path];
[TBLPROPERTIES (property_name=property_value,...)]
Create Table As (CTAS)
CREATE TABLE occupation_count STORED AS RCFile
AS SELECT COUNT(*), occupation FROM users GROUP BY occupation;
Create Table LIKE (CTL)
CREATE TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] <tablename> LIKE <sourcetable>
External Table
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE User(
user_id int, age int, gender string, occupration string)
ROW FORMAT DELIMETED
FIELDS TERMINATED BY ','
STORED AS TEXTFILE
LOCATION '/art/userinfo';
Hive Managed Table (/hive/warehouse)
use art;
CREATE TABLE movies (
movie_id INT,
movie_title STRING,
release_date STRING
)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
FIELDS TERMINATED BY '|'
STORED AS TEXTFILE;
Creating Temporary Table
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE LIKE customers;
Load Data to Hive Tables
LOAD DATA INPATH '/art/userinfo' INTO TABLE movies;
Truncate Tables
TRUNCATE TABLE <tablename>
Describe
describe <tablename>
describe extended <tablename>
describe formatted <tablename>
Hive Table Partitions and Bucketing
- Splits Data into Smaller, Manageable Parts
- Enables Performance Optimizations
External Table Without Partition
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE page_views
(logtime STRING, userid INT, ip STRING, page STRING, ref STRING, os STRING, os_ver STRING, agent STRING)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\t'
LOCATION '/art/logs/pv_ext/'
External Table With Partition
- With Partitioned Table Location is optional but helps in ETL job.
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE page_views_ext
(logtime STRING, userid INT, ip STRING, page STRING, ref STRING, os STRING, os_ver STRING, agent STRING)
PARTITIONED BY (y STRING, m STRING, d STRING)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\t'
LOCATION '/art/logs/pv_ext/';
Loading Data to External Table with Partition
ALTER TABLE page_views_ext ADD PARTITION (y='2013', m='07', d='11')
LOCATION '/art/logs/pv_ext/somedatafor_7_11';
Hive Managed Table with Partition
- Creating Partitions on your table helps in Query Performance
- Hive supports two partition models.
- Static Partition - Used when values for partition columns are well known
- Dynamic Partition - Used when values for partition columns are known only during loading data into a Hive table.
CREATE TABLE page_views (logtime STRING, userid INT, ip STRING, page STRING, ref STRING, os STRING, os_ver STRING, agent STRING)
PARTITIONED BY (y STRING, m STRING, d STRING)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\t';
-- Loading Data
LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH '/media/sf_VM_Share/LogFiles/log_2013805_16210.log'
OVERWRITE INTO TABLE page_views PARTITION (y='2013', m='08', d='05');
Dynamic Partition Inserts
CREATE TABLE views_stg (
viewid INT,
viewDateTimeStamp STRING,
applicationtype STRING,
page STRING
)
INSERT INTO views_stg PARITION(applicationtype='Web', page)
SELECT src.eventTime, src.userid, src.page WHERE applicationtype='Web'
- Static Partition should come first, followed by Dynamic Partitions
- Values of Dynamic Partition should come from source table
Use Following Hive Configuratin Settings if you plan to use Dynamic Inserts
set hive.exec.dynamic.partition=true;
set hive.optimize.sort.dynamic.partition=true;
set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=nonstrict;
set hive.exec.max.dynamic.partitions = 10000;
set hive.exec.max.dynamic.partitions.pernode = 10000;
Bucketing
- Bucketing is an approach to distribute or cluster table data
- Efficient Sampling
- Better performance with Map-side Joins
- Hive doesn’t control or enforce bucketing on data loaded into table
set hive.enforce.bucketing=true;
CREATE TABLE t1(a INT, b STRING, c STRING)
CLUSTERED BY (b) INTO 256 BUCKETS
Multiple Inserts
FROM <from_statement>
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE table1 SELECT
INESRT INTO table2 SELECT
Example,
FROM (SELECT * FROM movies WHERE release_date='8/23/2013') src
INSERT OVERWRITE table horror_movies SELECT * WHERE horror=1
INSERT INTO action_movies SELECT * WHERE action=1
Running HQL Scripts
hive -f hqlscript.hql --define queryTable=students
queryTable is passed as hiveVar
Running Hive Commands from Command Line
hive -e "use art; show tables"